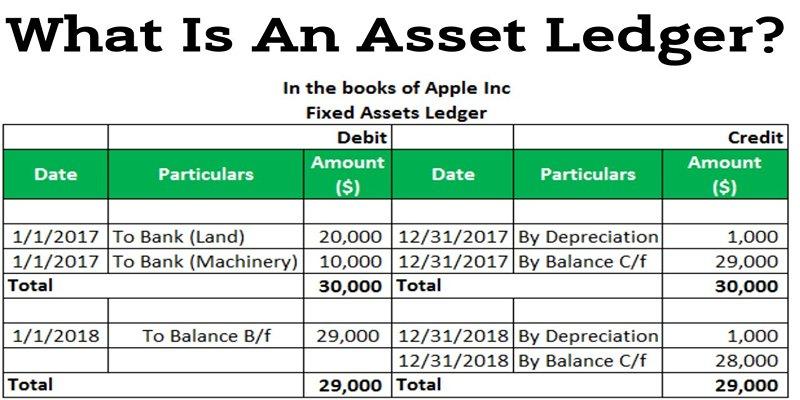
If you're running a business, tracking your assets can be key to staying organized and efficient. But what is an asset ledger, and why should you use one?
An asset ledger is a record-keeping system that helps businesses keep track of their resources, such as property, vehicles, machines, and inventory.
Not only does it help businesses stay organized and compliant with regulations, but it's also essential for managing day-to-day operations while helping to ensure accuracy in accounting processes.
In this blog post, we will explore the importance of having an asset ledger system at the vital center of any business enterprise.
Understanding the Asset Ledger
An asset ledger, a fixed asset register, is a detailed record of a company's fixed assets. These assets are a business's physical property, typically long-term investments, such as land, buildings, equipment, furniture, and vehicles. The asset ledger tracks important information about each fixed asset, including:
- Acquisition date
- Cost
- Depreciation schedule
- Current book value
By recording these details for each asset in a centralized ledger or register, companies can properly track and manage the value of their fixed assets over time. This is critical for accounting and tax reporting and making informed decisions about asset purchases, maintenance, and disposal. The asset ledger provides a comprehensive overview of a business's fixed assets to support financial management and strategic planning.
Examples of an Asset Ledger
An asset ledger is a detailed list of a company's assets that includes:
- Tangible assets: Physical assets such as equipment, property, vehicles, inventory, cash, etc. Each asset is listed along with details such as purchase date, cost, depreciation, and current market value.
- Intangible assets: Non-physical assets such as patents, copyrights, trademarks, goodwill, etc. The ledger will list each intangible asset and include details such as acquisition cost and remaining useful life.
The asset ledger allows a company to track the value of all assets and monitor depreciation and amortization. It provides an important overview of a company's financial position and can be used to make key business decisions regarding asset purchases or sales.
An up-to-date asset ledger is a critical business accounting and financial management task. The ledger should be reviewed and adjusted as needed on a regular schedule to ensure accuracy and support financial reporting.
Different types of asset ledgers are available.
An asset ledger is a comprehensive record of a company's assets. It tracks each asset from the time of acquisition to disposal and contains details such as:
- Asset identification (name, serial number, etc.)
- Date Acquired
- Cost
- Depreciation method and rate
- Accumulated depreciation
- Net book value
There are typically three main types of asset ledgers:
1. Manual ledger: Information is recorded manually in a physical ledger book. This is time-consuming and prone to errors.
2. Spreadsheet: Information is tracked in an electronic spreadsheet. This is an improvement over a manual ledger but can still be prone to errors and version control issues.
3. Asset management software: Dedicated asset management software provides an automated solution to track and manage assets. It has features like barcode/RFID scanning, depreciation calculation, and reporting. This is the optimal solution for most companies to maintain an accurate asset ledger.
What are the benefits of using an asset ledger?
An asset ledger provides organizations with several key benefits:
- Tracks physical assets. An asset ledger allows organizations to track their physical assets, including serial numbers, locations, and current ownership. This helps avoid lost or misplaced assets and ensures assets are properly accounted for.
- Manages depreciation and value. By tracking the purchase details and current value of assets, an asset ledger makes it easy to calculate depreciation and keep track of the financial value of an organization's assets. This is important for accounting and budgeting purposes.
- Enables auditing. A comprehensive asset ledger gives auditors the details necessary to verify an organization's assets and ensure proper accounting. This helps organizations maintain compliance and good financial practices.
- Informs decision-making. Knowing exactly what assets an organization has, their value, and current state helps leadership make more informed decisions about purchasing, maintenance, and resource allocation. The data in an asset ledger provides key insights to support strategic planning and optimization.
How to create your asset ledger
An asset ledger is a detailed record of the assets you own. Creating your asset ledger can be helpful for several reasons:
- It provides a comprehensive overview of your assets and their current values, which can be useful for insurance or financial planning.
- It allows you to track the appreciation or depreciation of your assets over time.
- It lets you stay organized by keeping all information about your assets in one place.
To create an asset ledger, here are the steps to follow:
1. List all your assets. This includes physical assets like your home, vehicles, electronics, jewelry, and financial assets like investments, savings accounts, and retirement funds.
2. Note the purchase date and price of each asset. For assets you already own, estimate the purchase date and price if you need to know the exact figures.
3. Determine the current market value of each asset. Check sources like Kelley Blue Book for vehicles or recent sales of comparable properties in your local real estate market.
4. Record the details for each asset. Include columns for the asset type, purchase date, purchase price, current market value, and any notes about the asset.
5. Track and update your asset ledger. Revisit your ledger at least once a year or whenever one of your assets is sold or experiences a significant change in value. Update the current market values and make other necessary changes to your records.
Following these steps will help you create and maintain an accurate asset ledger to gain a comprehensive overview of your financial situation. Regular updates can make your ledger an important tool for long-term financial planning.
FAQs
What is the assets and liabilities ledger?
The assets of a business include liquid resources such as cash and cash equivalents, money owed to the company from customers (accounts receivable), inventory of goods, investments, and long-term resources (fixed assets).
Using the double-entry bookkeeping method, a business's financial transactions are recorded in the general ledger to maintain an accurate and comprehensive record of its financial activity and position. This proven approach provides a robust system of checks and balances that helps minimize errors and ensures the book's balance.
What is a ledger example?
Ledger accounts capture the core elements of a business and its financial performance. Accounts such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventory reflect assets that can be converted into cash. Liabilities like accounts payable and debt represent obligations to creditors.
Stockholders' equity and revenue/expense accounts track the capital invested in and the financial results of the business. Specific expenses—the cost of goods sold, salaries, office expenses, depreciation, and income taxes—provide insights into a company's operational costs and profitability.
This structured set of accounts provides a comprehensive view of a company's financial position and results.
What are the two kinds of ledger?
The company's financial records are maintained through two key ledgers: nominal and private.
The nominal ledger tracks income, expenses, assets, and liabilities, providing an overview of the company's financial performance and position.
The private ledger contains confidential employee and ownership information, such as salary, wage, and capital accounts. These sensitive data are kept separate in the private ledger, allowing for appropriate internal access controls and privacy.
What is a ledger also called?
A ledger is the authoritative and permanent record of all financial transactions in accounting. All journal entries are meticulously recorded in the ledger, providing a comprehensive overview of account activity and balances.
The ledger's dual-entry system ensures precision, accuracy, and accountability in tracking debits and credits for each account. This core accounting tool provides a comprehensive and permanent record of a company's financial transactions and status.
Conclusion
Asset ledgers are critical components of any operation involving many tangible or intangible assets. Managing and monitoring these ledgers efficiently ensures any organization's assets' continued safety, accuracy, and accountability.
Not only do they help organizations to better manage their inventory and operations, but they also provide more transparency and security. With the right asset ledger system, organizations can gain an advantage over their competitors by keeping track of their investments and understanding the value of their existing assets.
More so, investing in an asset ledger presents a great opportunity for companies to reduce expenses associated with maintenance costs and product losses while increasing profit margins over time. Contact your financial advisor today to learn more about asset ledgers and how they could benefit your organization!